Soaking Up the Sun: Tips to Protect Yourself

Did you know?
- The skin is the largest organ in the body!
- Probably one of the easiest ways to prevent millions of cases of cancer each year is sunscreen!
Staying out of the sun is the best way to avoid sun damage, but most of us go outdoors regularly. So when you go outside, take these precautions:
- Always wear sunscreen. Apply it on your skin every day. Make it a habit, as you do with brushing your teeth.
- Avoid sun in the middle of the day, from about 10 a.m. to 3 p.m. The ultraviolet rays, which cause sunburn, are strongest during this time.
- Wear protective clothing. When you do go outdoors, especially for long periods in the middle of the day. Long sleeves and slacks, as well as a wide-brimmed hat, help protect your body against the sun’s harmful effects.
- Wear sunglasses that filter UV light.
The skin has three layers including:
- Epidermis: the outermost layer consisting of keratinocytes that are replaced approximately every 5 weeks with a new set of cells.
- Dermis: the layer that contains hair follicles, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands that produce oil-like lubricant for our skin and hair.
- Subcutis: the base layer which contains a layer of fat and connective tissue for insulation.
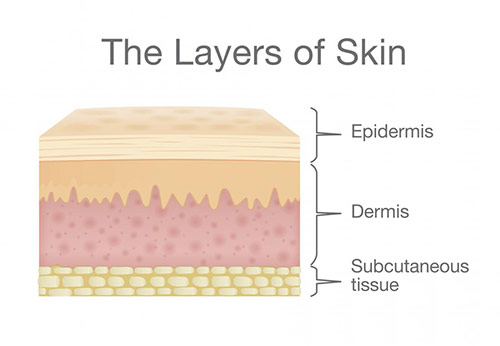
The skin is a very complex organ that forms our first layer of defense against temperature, infection, chemicals, and sunlight.
Sunlight contains two types of rays:
- Ultraviolet A (UVA) radiation: penetrates to the lowest layer of the epidermis where melanocytes produce melanin.
- Ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation: affects the upper layers of the epidermis and causes sunburn.
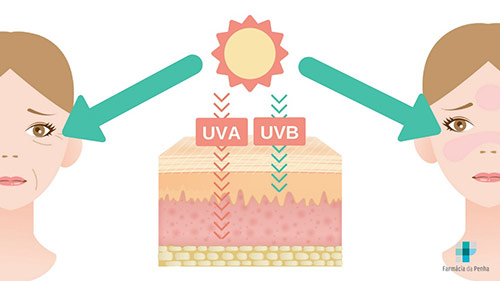
The tanning process:
- Melanin is a pigment produced in the epidermis, gives us our skin color, and helps protect us from burning.
- When exposed to UVA radiation, the pigmentation darkens resulting in a tan.
- Darker-skinned people tan more deeply due to increased amounts of melanin.
The risks of UV exposure:
- Increased exposure to sunlight, without proper protection, can lead to increased risk of skin cancer.
- UVB radiation has been associated with basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas.
- UVA radiation penetrates deeper into the epidermis and dermis, resulting in increased risk of melanoma.
- UVA radiation is also responsible for wrinkles.
It is important to stay active and spend time outside doing the activities we love, we just need to make sure that we are protecting ourselves along the way:
- Use sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB radiation. Be sure to check the label!
- Sunscreens with higher SPF provide more protection against the sun’s harmful rays.
- The World Health Organization recommends applying sunscreen 20 minutes before sun exposure with reapplication every 2 hours or after swimming/bathing.
- Limit your sun exposure between the hours of 10am and 4pm when the sun’s radiation is at its strongest.
- Use sunscreen even on cloudy days. It’s important to remember that even if you don’t feel like you are getting a sunburn (from UVB rays), the UVA rays can still be penetrating your skin and causing silent damage.
- Protect your eyes with sunglasses that provide 100% protection against UV radiation. Exposure to radiation can cause increased risk of corneal sunburn in addition to more long-term damage such as cataracts and macular degeneration.
- AVOID tanning beds, as UVA radiation is the main and most damaging ingredient.
Singh Snapshot
- The sun is very important for our health.
- Exposure to the sun provides us with an excellent source of vitamin D that is essential for good bone health.
- Finding a balance between sun exposure and protection may seem difficult but, if you take the above precautions, you’ll find yourself both protected and enjoying the amazing outdoors.

Acknowledgement
Samantha Erosa, M.D.
Resident Physician, PGY III
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
New York-Presbyterian
The University Hospital of Columbia and Cornell



Thank you Dr Singh. I very much enjoy receiving and reading your health articles. Your articles seem to be much more concise and intelligently composed then to most other unsolicited health tips.
Thanks again for the article on the important subject on sun tips.
I read all your articles whenever I see it on T.V.
K. Menon
The epidermis is a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. That is, the epidermis outermost layer consists of dead cells packed with the tough protein keratin. Like other epithelia, the epidermis lacks blood vessels and depends on the diffusion of nutrients from the underlying connective tissue.
Figure 5.14: Layers of the Epidermis. The epidermis of thick skin has five layers: stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum. The stratum basale is a single layer of cells primarily made of basal cells.
A great content. I want to talk. Please contact me by email divingcyprus[at]gmail.com.